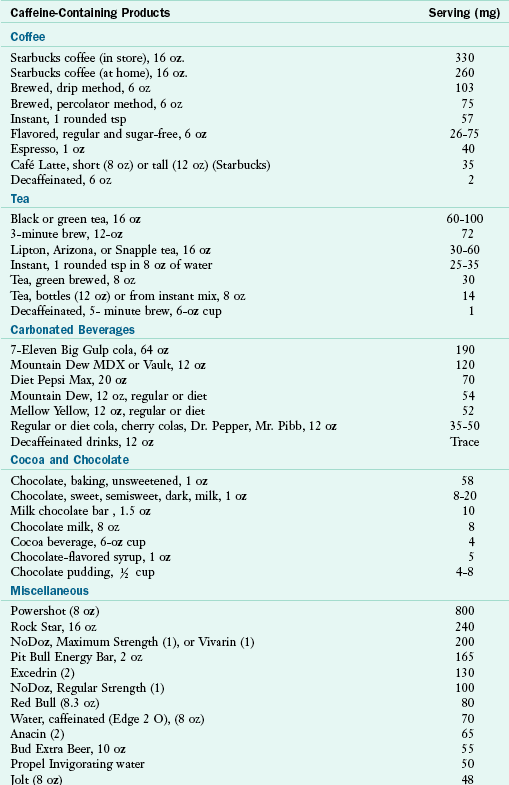
Nutritional Facts on Caffeine-Containing Products
Caffeine is similar in structure to adenosine, a chemical found in the brain that slows down its activity. Because the two compete, the more caffeine that is consumed, the less adenosine that is available up to a point. Caffeine temporarily heightens concentration and wards off fatigue. Within 30 to 60 minutes of drinking a cup of coffee, caffeine reaches peak concentrations in the bloodstream and takes 4 to 6 hours for its effects to wear off. The average American adult consumes about 200 mg of caffeine a day, and many may consume twice that level. It is generally safe to consume no more than the equivalent amount of caffeine in 1 to 2 cups of coffee daily during pregnancy or lactation. Individuals with heart disease and hypertension may benefit from a reduction in caffeine consumption. To reduce caffeine and its stimulant effects, monitor intake from foods and beverages listed below.