Nutritional Facts on Zinc
Zinc is an essential mineral that is found in almost every cell. It stimulates the activity of approximately 100 enzymes, which are substances that promote biochemical reactions in the body. Zinc supports immunity; is needed for wound healing; helps maintain the sense of taste and smell; is needed for deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis; and supports normal growth and development during pregnancy, childhood, and adolescence.
Zinc is found in a wide variety of foods. Atlantic oysters contain more zinc per serving than any other food, but red meat and poultry provide the majority of zinc in the American diet. Other good food sources include beans, nuts, certain seafood, whole grains, fortified breakfast cereals, and dairy products. Because zinc absorption is greater from a diet high in animal protein than a diet rich in plant proteins, vegetarians may become deficient if they are not monitored carefully. Phytates from whole-grain breads, cereals, legumes, and other products can decrease zinc absorption.

*Daily values (DVs) are reference numbers based on the recommended dietary allowance. They were developed to help consumers determine if a food contains a lot or a little of a specific nutrient. The DV for zinc is 15 mg. The %DV listed on the Nutrition Facts panel of food labels states the percentage of the DV provided in one serving.

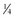 cup scrambled eggs
cup scrambled eggs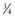 cup ready-to-eat breakfast cereal with 25% DV (3.8 mg zinc)
cup ready-to-eat breakfast cereal with 25% DV (3.8 mg zinc)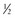 cup sliced peaches
cup sliced peaches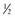 cup low-fat or fat-free milk
cup low-fat or fat-free milk cup carrot sticks
cup carrot sticks cup fresh steamed peas (0.8 mg zinc)
cup fresh steamed peas (0.8 mg zinc) cup fresh pineapple
cup fresh pineapple cup Trail mix (raisins, pecans, cashews, dried cranberries)
cup Trail mix (raisins, pecans, cashews, dried cranberries)