Dietary Reference Intakes
Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDA) and Adequate Intake (AI)a of Major Nutrients
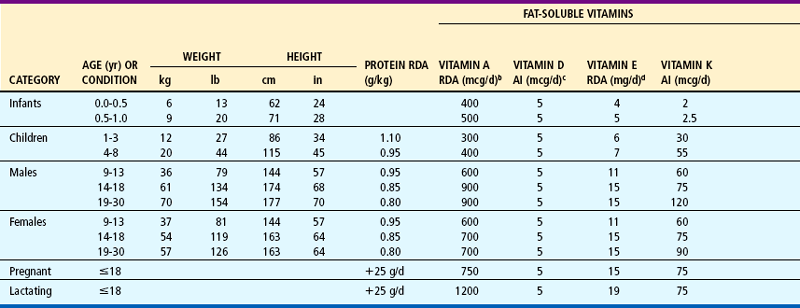
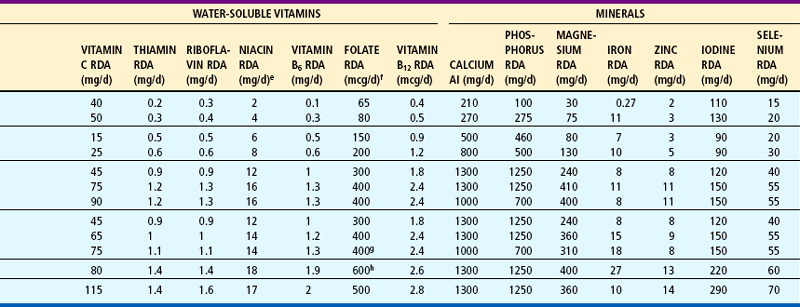
anote: For all nutrients, values for infants are AI.
bRetinol equivalent (RAE). 1 RAE = 1 mcg retinol
cCholecalciferol. 1 mcg cholecalciferol = 40 IU vitamin D. Assumes an absence of adequate exposure to sunlight.
dExpressed as α-tocopherol.
eExpressed as niacin equivalents (NE); except for infants <6 months of age, expressed as preformed niacin. 1 mg niacin = 60 mg tryptophan.
fExpressed as dietary folate equivalents (DFE); 1 DFE = 1 mcg food folate = 0.6 mcg folic acid from fortified food or as a supplement consumed with food = 5 mcg of a supplement taken on an empty stomach.
gIn view of evidence linking folate intake with neural tube defects in the fetus, it is recommended that all women capable of becoming pregnant consume 400 mcg from supplements or fortified foods in addition to intake of food folate from the diet.
hIt is assumed all women will continue consuming 400 mcg from supplements or fortified food until their pregnancy is confirmed and they enter prenatal care, which ordinarily occurs after the end of the preconceptional period—the critical time for formation of the neural tube.
Modified from the Dietary Reference Intake series, National Academy of Sciences, National Academies Press, 1997, 1998, 2000, 2001; and American Academy of Pediatrics: Pediatric nutrition handbook ed 5, Washington, DC, 2004, National Academies Press. National Academies Press
Estimated Safe and Adequate Daily Dietary Intakes of Selected Vitamins and Minerals*
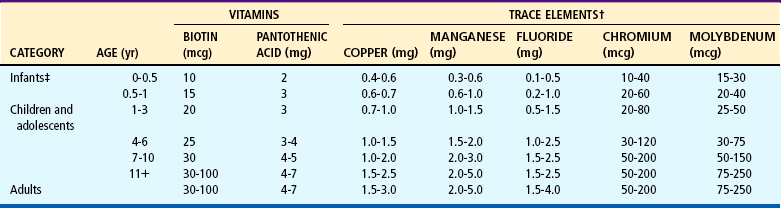
*Because there is less information on which to base allowances, these figures are not given in the main table of recommended dietary allowances and are provided here in the form of ranges of recommended intakes.
†Since the toxic levels for many trace elements may be only several times usual intakes, the upper levels for the trace elements given in this table should not be habitually exceeded.
‡For all nutrients, values for infants are adequate intake (AI).
From Food and Nutrition Board, National Research Council: Recommended dietary allowances, ed 10, Washington, DC, 1989, National Academy of Sciences. National Academy of Sciences
Estimated Sodium, Chloride, and Potassium Minimum Requirements of Healthy Persons*
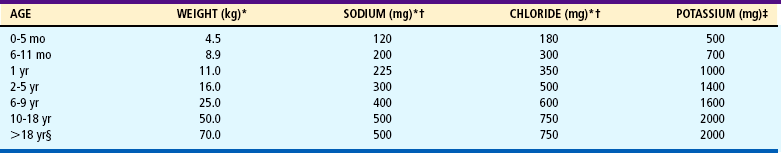
*No allowance has been included for large, prolonged losses from the skin through sweat
†There is no evidence that higher intakes confer any health benefit
‡Desirable intakes of potassium may considerably exceed these values (≈3500 mg for adults)
§No allowance included for growth. Values for those younger than 18 years of age assume a growth rate at the 50th percentile reported by the National Center for Health Statistics and averaged for males and females.
From Food and Nutrition Board, National Research Council: Recommended dietary allowances, ed 10, Washington, DC, 1989, National Academy of Sciences National Academy of Sciences
Median Heights and Weights and Estimated Energy Requirements (EERs)*
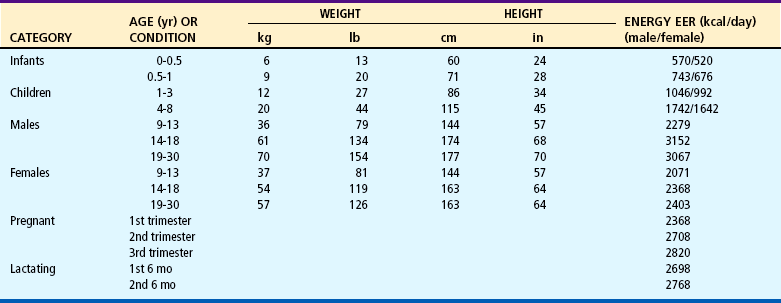
The estimated energy requirement (EER) represents an average dietary energy intake that will maintain energy balance in a healthy individual based on gender, age, weight, and height. The values given are based on an “active” person at the reference height and weight and the midpoint age for each age-group until 19.
Modified from the Dietary reference intake series, National Academy of Science, National Academies Press, 1997, 1998, 2000, 2001; and American Academy of Pediatrics: Pediatric nutrition handbook, ed 5, Washington, DC, 2004, National Academies Press. National Academies Press