85
Organization of the Endocrine System
The human body has two major control mechanisms, the nervous system and the endocrine system. While the nervous system can control and communicate rapidly with other systems, the endocrine system controls and communicates with the help of chemical messengers and is a much slower system. However, the effects of the endocrine system may be more prolonged and sustained.
Definition of a Hormone
The term “Hormone” is derived from a Greek word meaning “to excite or to arouse.” The term was first used by Ernest Henry Starling in 1905 in his first lecture delivered to the Royal Society. Starling along with Bayliss had discovered one of the first hormones called “Secretin” in 1902.
An endocrine hormone is a chemical substance that is produced by endocrine glands or a group of endocrine cells in response to certain stimuli and carried by blood to target tissues, where they exert their physiological actions.
The endocrine hormones are carried by the circulatory system to cells throughout the body, including the nervous system in some cases, where they bind with receptors and initiate many cell reactions. Some endocrine hormones affect many different types of cells of the body; for example, growth hormone (from the anterior pituitary gland) causes growth in most parts of the body and thyroxine (from the thyroid gland) increases the rate of many chemical reactions in almost all the body’s cells.
Coordination of Body Functions by Chemical Messengers
The multiple activities of the cells, tissues, and organs of the body are coordinated by the interplay of several types of chemical messenger systems:
1. Neurotransmitters are released by axon terminals of neurons into the synaptic junctions and act locally to control nerve cell functions.
2. Endocrine hormones are released by glands or specialized cells into the circulating blood and influence the function of target cells at another location in the body.
3. Neuroendocrine hormones are secreted by neurons into the circulating blood and influence the function of target cells at another location in the body.
4. Paracrines are secreted by cells into the extracellular fluid and affect neighboring target cells of a different type.
5. Autocrines are secreted by cells into the extracellular fluid and affect the function of the same cells that produced them.
6. Cytokines are peptides secreted by cells into the extracellular fluid and can function as autocrines, paracrines, or endocrine hormones. Examples of cytokines include the interleukins and other lymphokines that are secreted by helper cells and act on other cells of the immune system (see Chapter 25). Cytokine hormones (eg, leptin) produced by adipocytes are sometimes called adipokines.
In the next few chapters, we discuss mainly the endocrine and neuroendocrine hormone systems, keeping in mind that many of the body’s chemical messenger systems interact with one another to maintain homeostasis. For example, the adrenal medullae and the pituitary gland secrete their hormones primarily in response to neural stimuli.
The multiple hormone systems play a key role in regulating almost all body functions, including metabolism, growth and development, water and electrolyte balance, reproduction, and behavior. For instance, without growth hormone, a person would be a dwarf. Without thyroxine and triiodothyronine from the thyroid gland, almost all the chemical reactions of the body would become sluggish and the person would become sluggish as well. Without insulin from the pancreas, the body’s cells could use little of the food carbohydrates for energy. And without the sex hormones, sexual development and sexual functions would be absent.
Paracrine Secretions
Paracrine secretions (Figure 85-1) are those chemicals when released, exerts its effects on cells and tissues located in the neighborhood of its site of secretion; this by convention includes neurotransmitters. Paracrine hormones are dispersed by simple diffusion in the interstitial fluid and this restricts their action to short distances. Local enzymes in the vicinity usually rapidly inactivate the paracrine secretions thus preventing adequate entry into the blood stream.
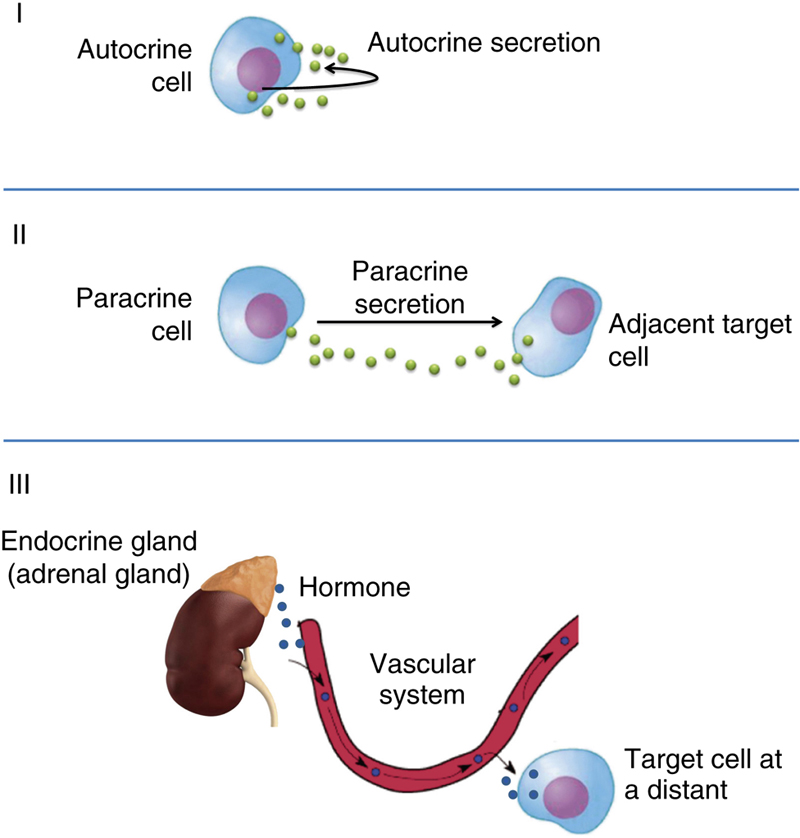
Figure 85-1 Illustration of autocrine (I), paracrine (II), and endocrine (III) secretions.
Examples of paracrine sections include the following:
1. Histamine released from cells in the stomach mucosa has a direct influence on the parietal cells of the oxyntic glands, causing an increase in acid secretion.
2. Neurotransmitters, such as acetylcholine, act on the parietal cells in the stomach mucosa causing an increase in acid secretion.
3. Prostaglandins—PGE2 is responsible for cervical dilatation at the time of childbirth (parturition).
Autocrine Secretions
Autocrine secretions are chemicals which are secreted by specific cells into the extracellular fluid surrounding the cell and which acts upon the very cells that secrete it (Figure 85-1).
Examples of autocrine secretions are as follows:
1. Norepinephrine that is released by neurons in the adrenal medulla further inhibits norepinephrine release by those cells.
2. Insulin released from β cells in the pancreas has an inhibitory effect on insulin secreted by these β cells, which is independent of glucose levels in the blood.
Location of Major Endocrine Organs
Figure 85-2 shows the anatomical loci of the major endocrine glands and endocrine tissues of the body, except for the placenta, which is an additional source of the sex hormones. Table 85-1 provides an overview of the different hormone systems and their most important actions.

Figure 85-2 Anatomical loci of the principal endocrine glands and tissues of the body.
Table 85-1
Endocrine Glands, Hormones, and Their Functions and Structure
| Gland/Tissue | Hormones | Major Functions | Chemical Structure |
| Hypothalamus (Chapter 87) | Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) | Stimulates secretion of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and prolactin | Peptide |
| Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) | Causes release of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) | Peptide | |
| Growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) | Causes release of growth hormone | Peptide | |
| Growth hormone-inhibitory hormone (GHIH) | Inhibits release of growth hormone | Peptide | |
| (somatostatin) | |||
| Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) | Causes release of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) | Peptide | |
| Dopamine or prolactin-inhibiting factor (PIF) | Inhibits release of prolactin | Amine | |
| Anterior pituitary (Chapter 87) | Growth hormone | Stimulates protein synthesis and overall growth of most cells and tissues | Peptide |
| TSH | Stimulates synthesis and secretion of thyroid hormones (thyroxine and triiodothyronine) | Peptide | |
| ACTH | Stimulates synthesis and secretion of adrenocortical hormones (cortisol, androgens, and aldosterone) | Peptide | |
| Prolactin | Promotes development of the female breasts and secretion of milk | Peptide | |
| FSH | Causes growth of follicles in the ovaries and sperm maturation in Sertoli cells of testes | Peptide | |
| LH | Stimulates testosterone synthesis in Leydig cells of testes; stimulates ovulation, formation of corpus luteum, and estrogen and progesterone synthesis in ovaries | Peptide | |
| Posterior pituitary (Chapter 88) | Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) (also called vasopressin) | Increases water reabsorption by the kidneys and causes vasoconstriction and increased blood pressure | Peptide |
| Oxytocin | Stimulates milk ejection from breasts and uterine contractions | Peptide | |
| Thyroid (Chapter 89) | Thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) | Increases the rates of chemical reactions in most cells, thus increasing body metabolic rate | Amine |
| Calcitonin | Promotes deposition of calcium in the bones and decreases extracellular fluid calcium ion concentration | Peptide | |
| Adrenal cortex (Chapter 91) | Cortisol | Has multiple metabolic functions for controlling metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats; also has antiinflammatory effects | Steroid |
| Aldosterone | Increases renal sodium reabsorption, potassium secretion, and hydrogen ion secretion | Steroid | |
| Adrenal medulla (Chapter 92) | Norepinephrine, epinephrine | Same effects as sympathetic stimulation | Amine |
| Pancreas (Chapter 93) | Insulin (β cells) | Promotes glucose entry in many cells, and in this way controls carbohydrate metabolism | Peptide |
| Glucagon (α cells) | Increases synthesis and release of glucose from the liver into the body fluids | Peptide | |
| Parathyroid (Chapter 90) | Parathyroid hormone (PTH) | Controls serum calcium ion concentration by increasing calcium absorption by the gut and kidneys and releasing calcium from bones | Peptide |
| Testes (Chapter 94) | Testosterone | Promotes development of male reproductive system and male secondary sexual characteristics | Steroid |
| Ovaries (Chapter 96) | Estrogens | Promotes growth and development of female reproductive system, female breasts, and female secondary sexual characteristics | Steroid |
| Progesterone | Stimulates secretion of “uterine milk” by the uterine endometrial glands and promotes development of secretory apparatus of breasts | Steroid | |
| Placenta (Chapter 98) | Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) | Promotes growth of corpus luteum and secretion of estrogens and progesterone by corpus luteum | Peptide |
| Human somatomammotropin | Probably helps promote development of some fetal tissues as well as the mother’s breasts | Peptide | |
| Estrogens | See actions of estrogens from ovaries | Steroid | |
| Progesterone | See actions of progesterone from ovaries | Steroid | |
| Kidney (Chapter 76) | Renin | Catalyzes conversion of angiotensinogen to angiotensin I (acts as an enzyme) | Peptide |
| 1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol | Increases intestinal absorption of calcium and bone mineralization | Steroid | |
| Erythropoietin | Increases erythrocyte production | Peptide | |
| Heart (Chapter 51) | Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) | Increases sodium excretion by kidneys, reduces blood pressure | Peptide |
| Stomach (Chapter 67) | Gastrin | Stimulates HCl secretion by parietal cells | Peptide |
| Small intestine (Chapter 68) | Secretin | Stimulates pancreatic acinar cells to release bicarbonate and water | Peptide |
| Cholecystokinin (CCK) | Stimulates gallbladder contraction and release of pancreatic enzymes | Peptide | |
| Adipocytes | Leptin | Inhibits appetite, stimulates thermogenesis | Peptide |


Feedback Control of Hormone Secretion
Levels of Control within the Endocrine System
Although the plasma concentrations of many hormones fluctuate in response to various stimuli that occur throughout the day, all hormones studied thus far appear to be closely controlled.
There are several control mechanisms that exist to regulate the levels of hormones very precisely.
An example to review is the hypophysiotrophic hormones with a three-level sequence to understand the different levels of hormonal control.
There are three levels of feedback control as indicated in Figure 85-3; these are as follows:
1. Long loop feedback control: In this case, the hormone secreted by the peripheral endocrine gland provides a negative feedback to the hypothalamus or the anterior pituitary gland. For example, excess levels of thyroxine will inhibit both the anterior pituitary gland from secreting thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and the hypothalamus from secreting thyrotropin releasing hormone.
2. Short loop feedback control: In this mechanism, the anterior pituitary hormone in plasma provides a negative feedback to the hypothalamus, decreasing the secretion of releasing hormones.
3. Ultrashort loop feedback control: In this mechanism, the releasing hormones themselves have a negative feedback influence on the hypothalamus thus decreasing the secretion of the hypothalamic hormones.
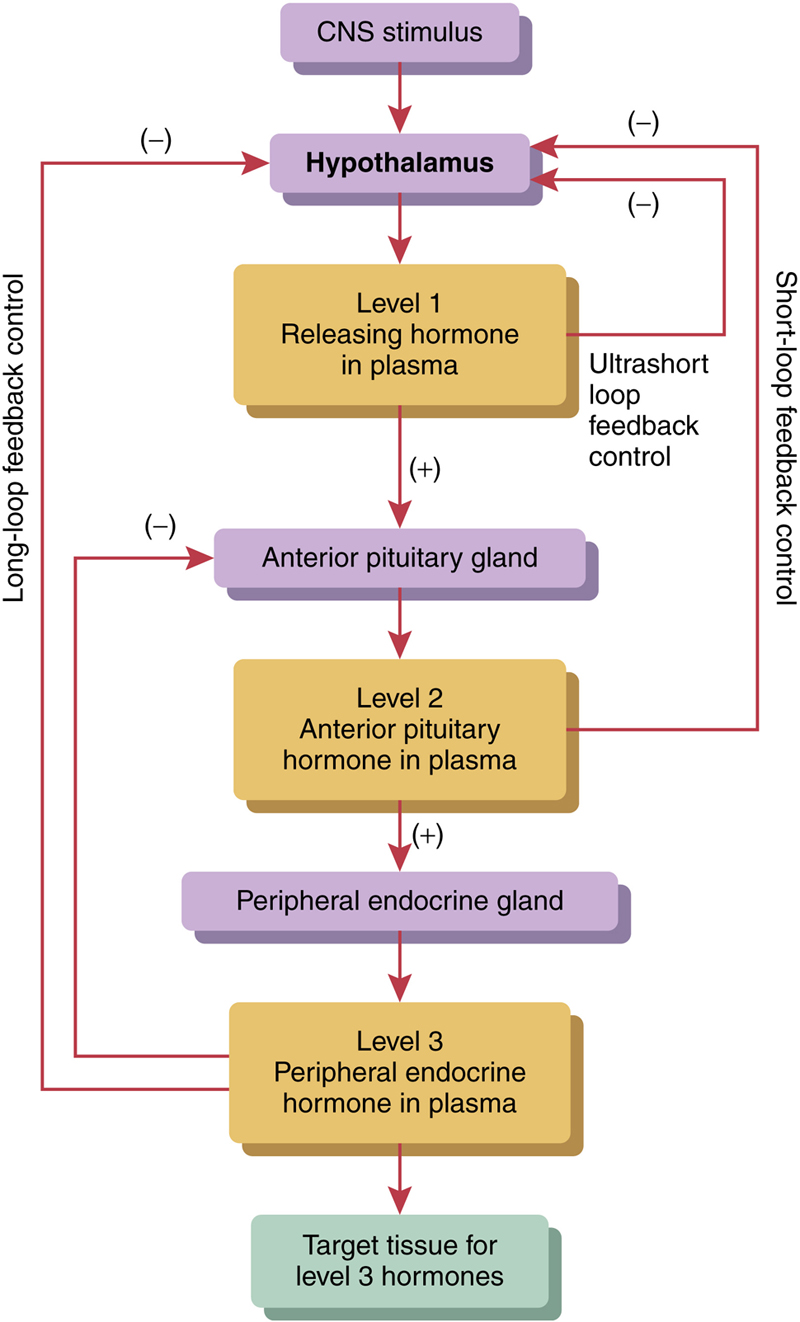
Figure 85-3 Levels of control in the endocrine system.
Negative Feedback Prevents Overactivity of Hormone Systems
In most instances, hormonal control is exerted through negative feedback mechanisms (described in Chapter 1) that ensure a proper level of hormone activity at the target tissue. After a stimulus causes release of the hormone, conditions or products resulting from the action of the hormone tend to suppress its further release. In other words, the hormone (or one of its products) has a negative feedback effect to prevent oversecretion of the hormone or overactivity at the target tissue.
The controlled variable is sometimes not the secretory rate of the hormone but the degree of activity of the target tissue. Therefore, only when the target tissue activity rises to an appropriate level will feedback signals to the endocrine gland become powerful enough to slow further secretion of the hormone. Feedback regulation of hormones can occur at all levels, including gene transcription and translation steps involved in the synthesis of hormones and steps involved in processing hormones or releasing stored hormones.
Examples of negative feedback mechanisms:
1. Negative feedback by plasma levels of thyroid hormones on the hypothalamus and the anterior pituitary gland (Figure 85-4).
2. Negative feedback by plasma cortisol levels on the hypothalamus and the anterior pituitary gland.

Figure 85-4 Example of negative feedback inhibition.
Surges of Hormones Can Occur with Positive Feedback
In a few instances, positive feedback occurs when the biological action of the hormone causes additional secretion of the hormone. One example of positive feedback is the surge of luteinizing hormone (LH) that occurs as a result of the stimulatory effect of estrogen on the anterior pituitary before ovulation. The secreted LH then acts on the ovaries to stimulate additional secretion of estrogen, which in turn causes more secretion of LH. Eventually, LH reaches an appropriate concentration and typical negative feedback control of hormone secretion is then exerted.
Cyclical Variations Occur in Hormone Release
Superimposed on the negative and positive feedback control of hormone secretion are periodic variations in hormone release that are influenced by seasonal changes, various stages of development and aging, the diurnal (daily) cycle, and sleep. For example, the secretion of growth hormone is markedly increased during the early period of sleep but is reduced during the later stages of sleep. In many cases, these cyclical variations in hormone secretion are due to changes in activity of neural pathways involved in controlling hormone release.
Clinical Conditions Associated with Altered Hormone Release
Various clinical conditions can manifest if the secretion of hormones is altered either due to hyposecretion or hypersecretion. Table 85-2 summarizes the various clinical conditions associated with each endocrine gland.
Table 85-2
Clinical Conditions Associated with Hyposecretion and Hypersecretion of Each Endocrine Gland
| S. No. | Endocrine Gland and Hormones | Clinical Conditions Hyposecretion | Clinical Conditions Hypersecretion |
| 1. | Anterior pituitary gland | ||
|
• Growth hormone
|
Pituitary dwarfism | Gigantism in children | |
|
• All hormones
|
Panhypopituitarism | Acromegaly in adults | |
| Posterior pituitary gland | |||
|
• Antidiuretic hormone
|
Diabetes insipidus | ||
| 2. | Thyroid gland | Cretinism in children Myxedema in adults |
Graves’ disease |
| 3. | Parathyroid gland | Hypoparathyroidism | Hyperparathyroidism |
| 4. | Pancreas | ||
|
• Insulin
|
Type I Diabetes mellitus | Hyperinsulinism | |
| Type II Diabetes mellitus | |||
| 5. | Adrenal gland | ||
|
• Glucocorticoid
|
Cushing’s syndrome | ||
|
• Mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids
|
Addison’s disease | Pheochromocytoma | |
|
• Epinephrine and norepinephrine
|
