Practical clinic procedures
Dermatologists make use of several diagnostic and therapeutic procedures in their everyday clinical practice.
Diagnostic procedures
The ability to diagnose a skin disease is improved by the use of better methods of observing lesions and by appropriate use of samples for laboratory investigation. Patch tests and prick tests are described on page 126.
Dermoscopy
A hand lens helps when looking at small lesions such as nits on hair shafts (Fig. 1) or scabetic burrows, but dermoscopy gives added information, especially for pigmented lesions. Dermoscopy employs a ×10 magnification illuminated lens system, which can visualize a lesion after the application of a drop of oil or water between the skin and the applied lens. Detailed visualization of the epidermal structures is possible, particularly the pigment network (Fig. 2). Analysis takes account of:
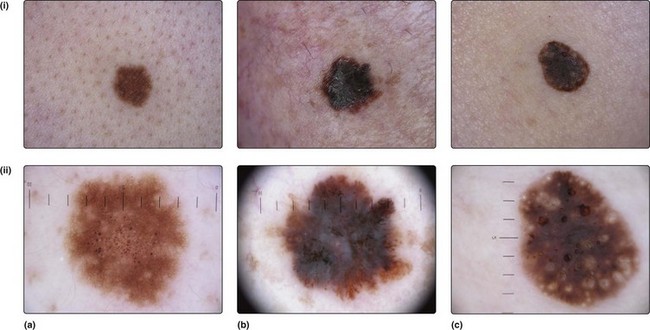
Fig. 2 Use of the dermoscope in (a) a benign melanocytic naevus, (b) a malignant melanoma, (c) a seborrhoeic wart.
Comparison of the macroscopic (i) and dermoscopic (ii) appearances in each case.
Dermoscopy allows an opinion to be made about the nature and malignant potential of the lesion.
Microbiology samples
Swabs for bacterial and viral culture should be sampled from areas showing pus or exudation. Scrapings for fungal microscopy and culture are obtained by the following techniques:
 The active scaly edge of an eruption is sampled using a disposable scalpel blade held vertically to the skin.
The active scaly edge of an eruption is sampled using a disposable scalpel blade held vertically to the skin.
 Nail samples are taken from the distal portion or from debris beneath the nail using clippers or a scalpel.
Nail samples are taken from the distal portion or from debris beneath the nail using clippers or a scalpel.
 Hair sampling requires plucking of hairs as the hair root is often infected (a scalp scraping is also worthwhile).
Hair sampling requires plucking of hairs as the hair root is often infected (a scalp scraping is also worthwhile).
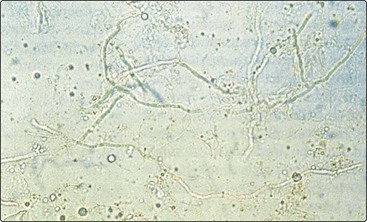
Samples are taken onto a small sheet of black paper or a microscope slide (Fig. 3). Direct microscopy of scrapings mounted in 20% potassium hydroxide solution will show hyphae (Fig. 4).
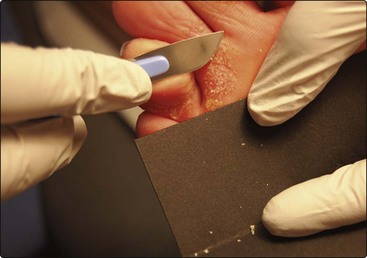
Fig. 3 Take a scraping from the edge of an area of suspected fungal infection by using a disposable scalpel blade.
Demonstrating the acarus of scabies
Dermatologists sometimes need to demonstrate the mite to themselves or their patients (p. 62). This can be achieved by:
Wood’s light examination
Wood’s light is a hand-held ultraviolet A (UVA) source that can be shone on the skin in a darkened room to diagnose certain skin diseases that show particular patterns of fluorescence in UV radiation. It is used especially for:
Dermographism
Stroking the skin in patients with symptomatic dermographism will induce whealing (p. 76). Cold-induced urticaria can be provoked by the application of an ice cube to the skin. Rubbing a lesion of urticaria pigmentosa will produce a localized wheal (p. 116).
Doppler studies
The measurement of the ankle/brachial blood pressure index (ABPI) is essential in the management of patients with leg ulcers (p. 73). The ABPI must be >0.8 for compression therapy.
Therapeutic procedures
Dermatologists use some non-surgical techniques in their clinical work. Surgical methods and cryotherapy are dealt with elsewhere (p. 111).
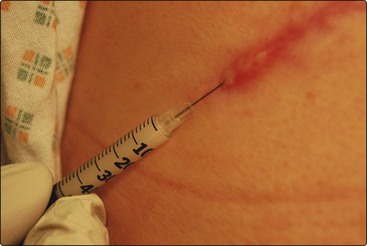
Intralesional steroid injection
The injection of steroid into the skin is useful in the management of several diseases, including:
Triamcinolone acetonide (10 mg/mL) is normally used in an insulin syringe, which has an integral needle. An injection of 0.1–1.0 mL of the solution is given into the mid or deep dermis (Fig. 5). The main side-effects are skin atrophy, hypopigmentation and telangiectasia. Occasionally, injection of other substances into the skin is used, e.g. bleomycin for viral warts (p. 53).
Paring of skin
The paring down of hyperkeratotic areas on the hands or feet using a disposable scalpel often helps in:
 diagnosis, as it can reveal the underlying lesion, e.g. the punctate thrombosed capillaries of a viral wart or a small haematoma within the epidermis (such as that produced by the friction of shoes on the heel)
diagnosis, as it can reveal the underlying lesion, e.g. the punctate thrombosed capillaries of a viral wart or a small haematoma within the epidermis (such as that produced by the friction of shoes on the heel)
 therapy, e.g. for callosities under the metatarsals, by reducing the pressure that results from the callus.
therapy, e.g. for callosities under the metatarsals, by reducing the pressure that results from the callus.
On the feet, callosities often develop as a result of the interaction of external forces and an abnormal anatomy of the foot. The advice of a chiropodist or podiatrist will usually be helpful.
Use of caustics
Xanthelasma around the eyes (p. 84) can be treated by the careful application of the caustic trichloroacetic acid (30–50%) solution on an almost dry cotton applicator. Great care is needed to protect the eyes. The treatment should be carried out only by those experienced in the procedure. The xanthelasma turns white with ‘frosting’ within seconds of application of the acid, and subsequently the treated skin peels off over a period of days.
Procedures in the skin clinic
 Dermoscopy is useful in deciding whether or not a pigmented lesion might be a malignant melanoma.
Dermoscopy is useful in deciding whether or not a pigmented lesion might be a malignant melanoma.
 Skin scrapings for mycology should be taken from the edge of a suspect area using a disposable scalpel blade onto a piece of black paper.
Skin scrapings for mycology should be taken from the edge of a suspect area using a disposable scalpel blade onto a piece of black paper.
 Wood’s light can show the extent of vitiligo or diagnose erythrasma or tinea capitis.
Wood’s light can show the extent of vitiligo or diagnose erythrasma or tinea capitis.
 Intralesional triamcinolone is a useful treatment for alopecia areata, keloid, acne cysts and other diseases. Skin atrophy is a potential side-effect.
Intralesional triamcinolone is a useful treatment for alopecia areata, keloid, acne cysts and other diseases. Skin atrophy is a potential side-effect.
 Paring of skin can reveal the underlying condition, e.g. a viral wart, or be a treatment for callosity.
Paring of skin can reveal the underlying condition, e.g. a viral wart, or be a treatment for callosity.
 Application of caustic: trichloroacetic acid is used with care in the treatment of xanthelasma.
Application of caustic: trichloroacetic acid is used with care in the treatment of xanthelasma.